Uc External Location Storage Credentials
Managed Table Locations in Unity Catalog🔗
- External Metastore Location is provided.
If the metastore storage account is provided by us, then all the catalog, schema and tables is created under this location. At catalog level the location doesnt matter its optional.
- If Metastore location is not provided.
In this case we need to provide the location at catalog level to create tables. This is mandatory.
Creating a container for our catalog🔗
All data for the managed tables will be stored under this external location if we dont specify it at the schema level.
How things get affected when providing location at different levels in UC?🔗
1️⃣ External location at Metastore level
When you create a Metastore, you must give it a storage root. Example:
CREATE METASTORE my_metastore
LOCATION 'abfss://uc-metastore@<storageaccount>.dfs.core.windows.net/'
This location is the default root for managed tables if no other path is specified.
Any catalog/schema/table created as managed without its own external location will fall back here.
👉 So think of it like a global default storage for all managed tables across catalogs.
2️⃣ External location at Catalog level
When you create a catalog, you can optionally give it its own external location:
Now, managed tables inside this catalog will go under this catalog-specific external location (instead of the metastore root).
This is useful for separating zones (raw, curated, gold) into their own ADLS containers/folders.
👉 So catalogs can “override” the metastore root location.
3️⃣ External Tables vs Managed Tables
Managed Table: Unity Catalog controls the data lifecycle.
Data Deletion Timeline: While the data deletion is initiated immediately, the actual purging of the data files from cloud storage may not be instantaneous. Databricks documentation indicates that the files are typically deleted within a retention period, often around 7 days, though this can sometimes be influenced by Delta Lake's default log retention (e.g., 30 days). Running a VACUUM command can also accelerate the deletion of unreferenced data files.
Data lives in either: The Metastore storage root, if no catalog location is set. The Catalog’s external location, if provided.
External Table: You explicitly provide a LOCATION when creating the table.
Example
-- Metastore root
CREATE METASTORE main_metastore
LOCATION 'abfss://uc-metastore@stacc1.dfs.core.windows.net/';
-- Catalog with its own location
CREATE CATALOG raw_data
USING MANAGED LOCATION raw_external;
-- Managed table in raw_data (goes to raw_external)
USE CATALOG raw_data;
CREATE TABLE users_managed (id INT, name STRING) USING DELTA;
-- External table (explicit path overrides everything)
CREATE TABLE users_external (id INT, name STRING)
USING DELTA
LOCATION 'abfss://special@stacc2.dfs.core.windows.net/custom_path/';
Creating External Location For Catalog🔗
- Creating the Storage Credential
This is basically using previous UC Connector to connect to our new storage container for the catalog data.
- Create the external location
CREATE EXTERNAL LOCATION ext_catalog_dev
URL 'abfss://data@adbvedanthnew.dfs.core.windows.net/data/catalog'
WITH (STORAGE CREDENTIAL `uc-data-storage`);
CREATE CATALOG dev_ext MANAGED LOCATION 'abfss://data@adbvedanthnew.dfs.core.windows.net/data/catalog' COMMENT 'This is external storage catalog'
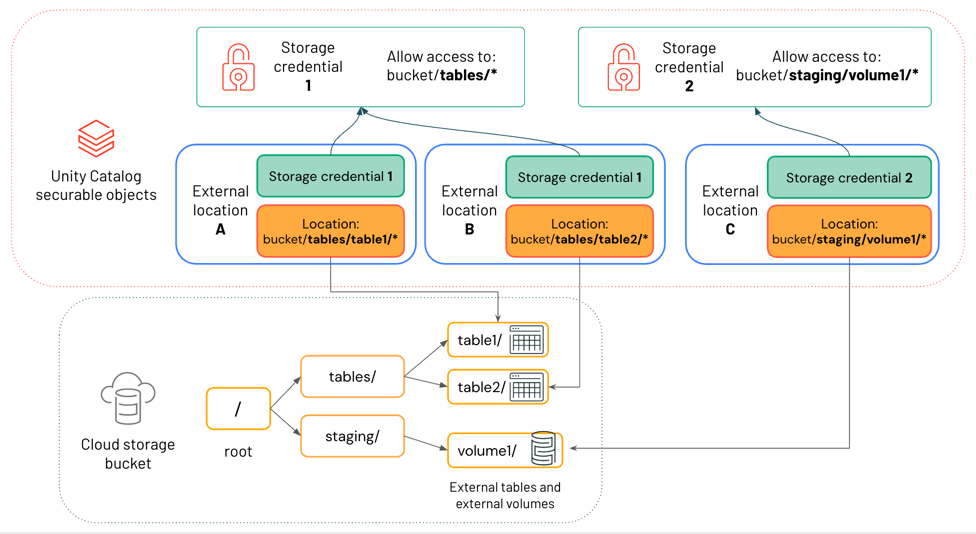
Visual Architecture of External Location, Storage Credential and Volume Access🔗
Both managed storage locations and storage locations where external tables and volumes are stored use external location securable objects to manage access from Databricks. External location objects reference a cloud storage path and the storage credential required to access it. Storage credentials are themselves Unity Catalog securable objects that register the credentials required to access a particular storage path. Together, these securables ensure that access to storage is controlled and tracked by Unity Catalog.