What is Airflow?
What is Apache Airflow?🔗
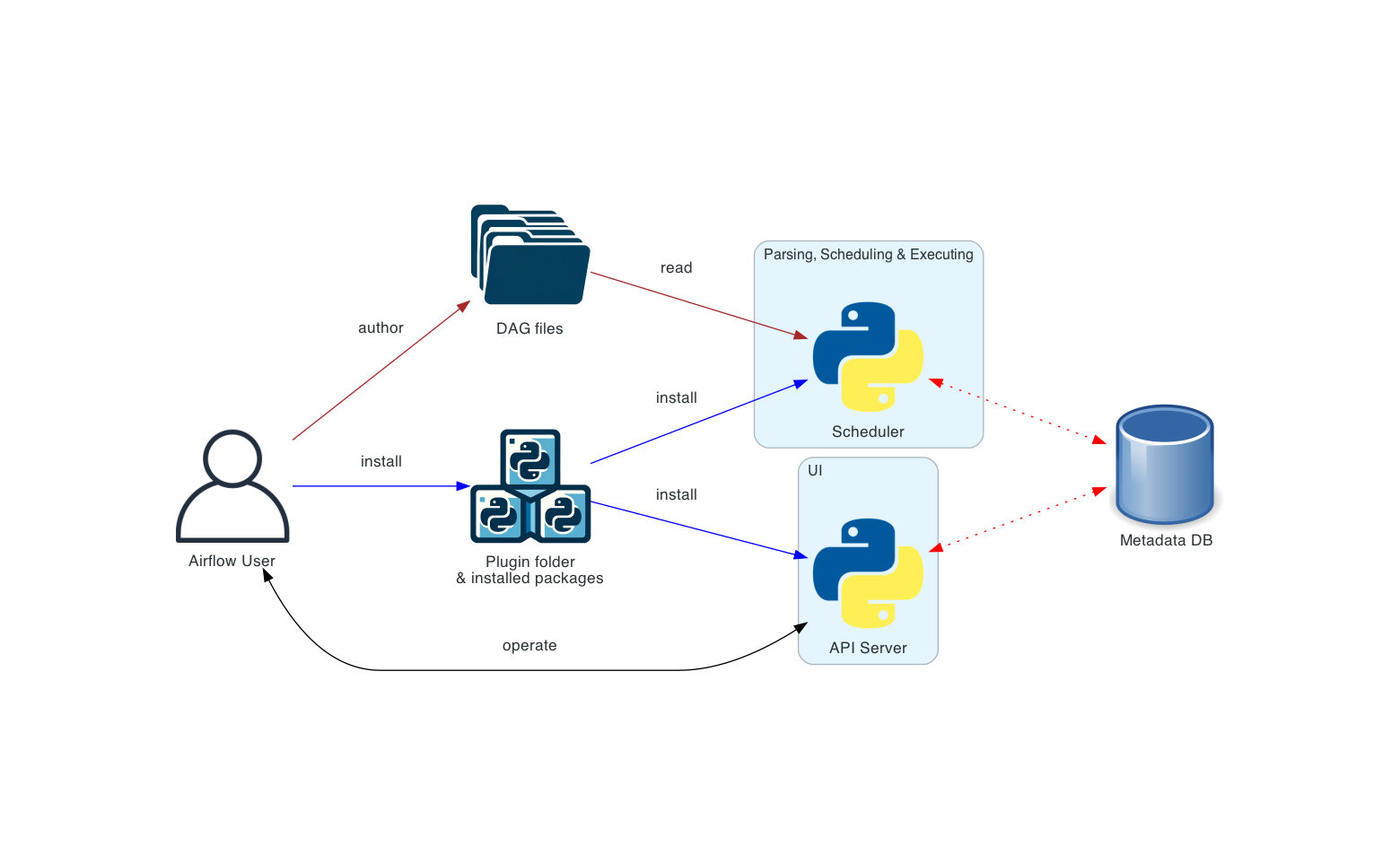
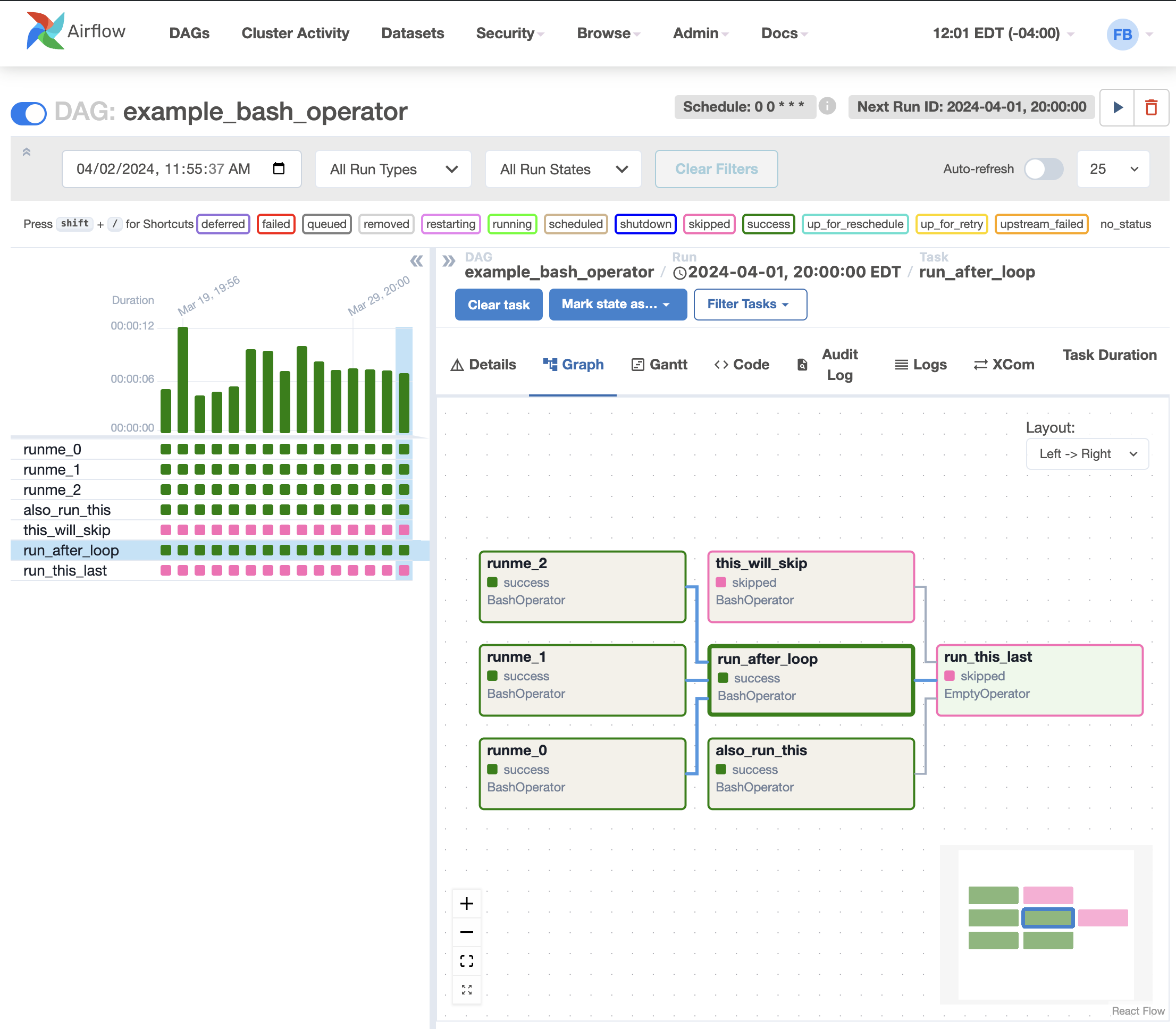
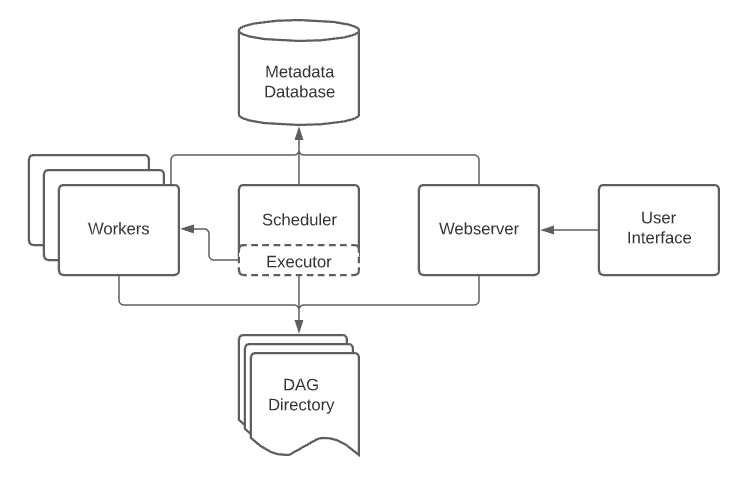
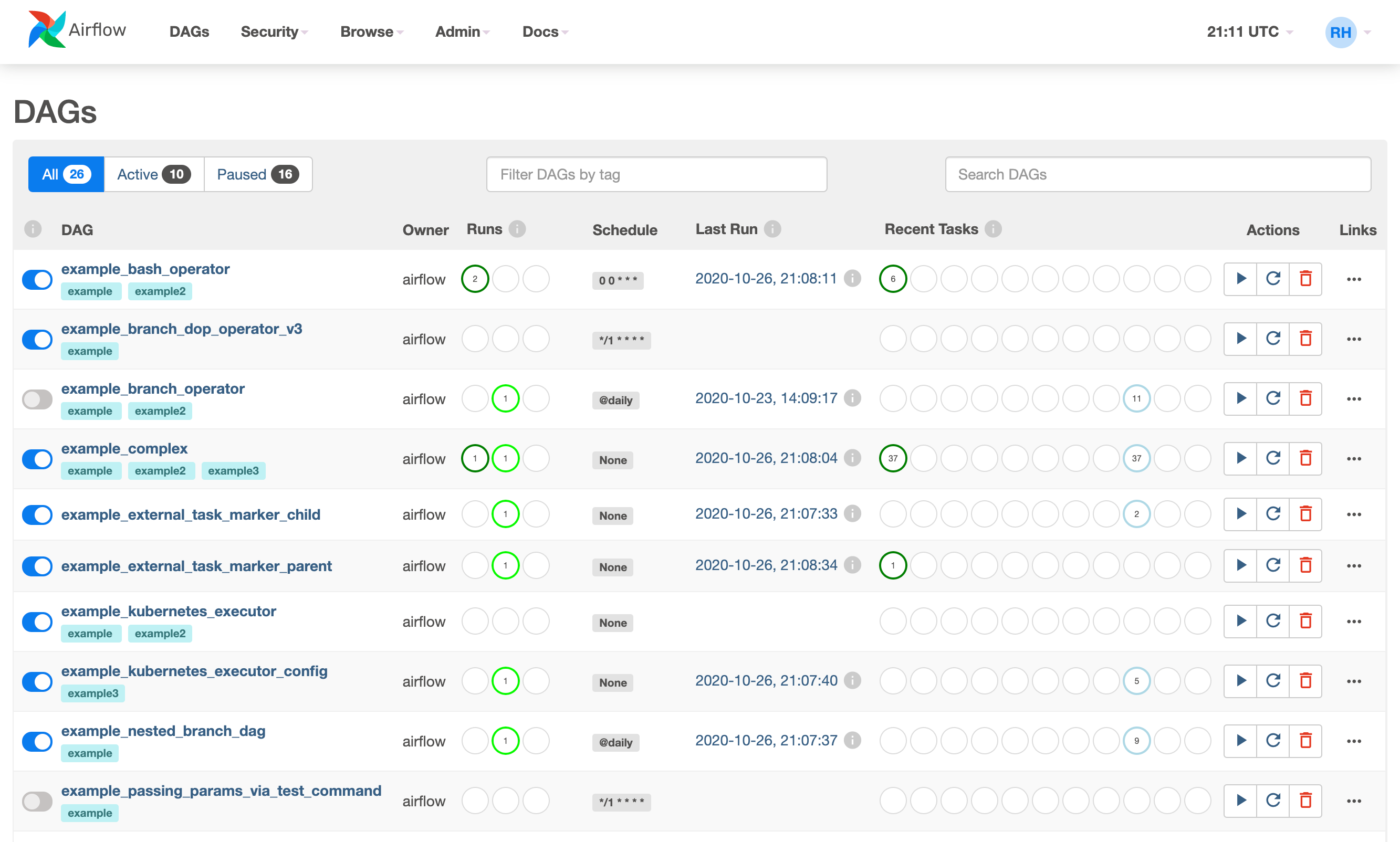
Apache Airflow is an open-source workflow orchestration platform used to author, schedule, and monitor batch workflows (data pipelines). It lets you define what should run, in what order, and when, while handling retries, failures, dependencies, and visibility.
Core Idea🔗
Airflow coordinates work across systems. It does not process data itself. Instead, it triggers and monitors tools like Spark, Databricks, dbt, warehouses, APIs, and scripts.
Key Concepts🔗
1) DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)🔗
- A DAG defines a workflow
- Written in Python
-
Describes:
-
Tasks
- Dependencies
- Schedule
- “Acyclic” means no loops
Example flow:
2) Tasks and Operators🔗
- A task is one unit of work
- Operators define how that task runs
Common operators:
PythonOperator– run Python logicBashOperator– run shell commandsSparkSubmitOperator– submit Spark jobsDatabricksRunNowOperator– trigger Databricks jobs- Warehouse operators (Snowflake, Redshift, BigQuery)
3) Scheduler🔗
- Determines when a DAG run should start
-
Handles:
-
Cron schedules
- Dependencies
- Backfills
- Catchup logic
4) Executor🔗
- Controls how tasks are executed
-
Common executors:
-
SequentialExecutor (local testing)
- LocalExecutor
- CeleryExecutor (distributed workers)
- KubernetesExecutor (cloud-native)
5) Web UI🔗
- Visual DAG graphs
- Task execution history
- Logs per task attempt
- Retry, clear, and rerun controls
- SLA monitoring
What Airflow Is Good At🔗
- Orchestrating complex batch pipelines
- Managing dependencies across systems
- Handling retries and failures
- Scheduling jobs reliably
- Providing operational visibility
What Airflow Is NOT🔗
- Not a data processing engine
- Not a streaming engine
- Not a replacement for Spark, Flink, or SQL engines
Airflow only orchestrates those systems.
Typical Use Cases🔗
- Daily ETL pipelines
- Triggering Spark or Databricks jobs
- Running dbt models in sequence
- ML training and scoring pipelines
- Data quality and validation checks
- SLA-based alerting
Where Airflow Fits in a Data Architecture🔗

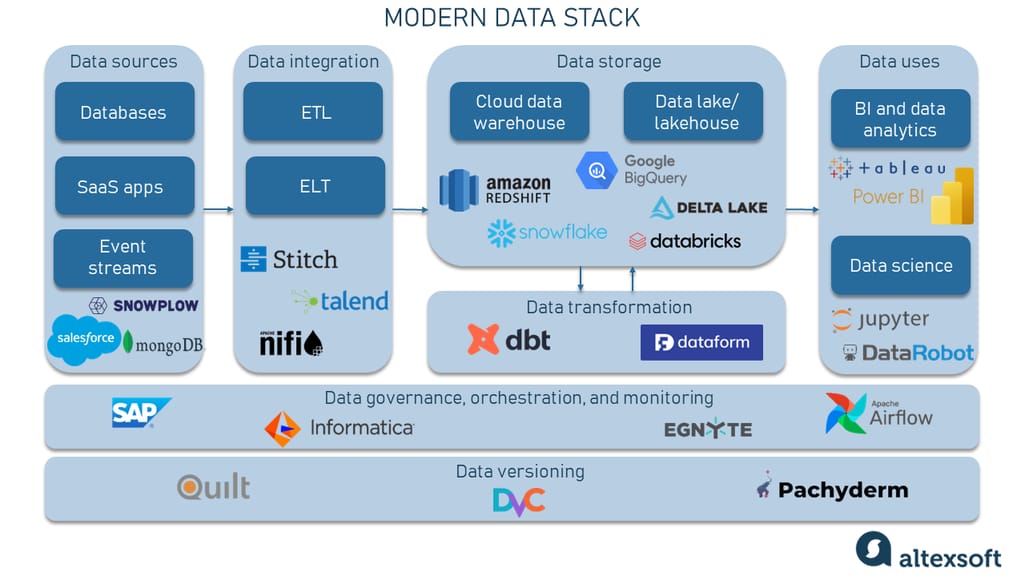
Example:
Sources (APIs, Kafka, DBs)
↓
Airflow
↓
Spark / Databricks / dbt
↓
Data Warehouse / Lakehouse
↓
BI / Analytics / ML
Airflow sits above compute systems and coordinates them.